Walk Through a Hydroelectric Project

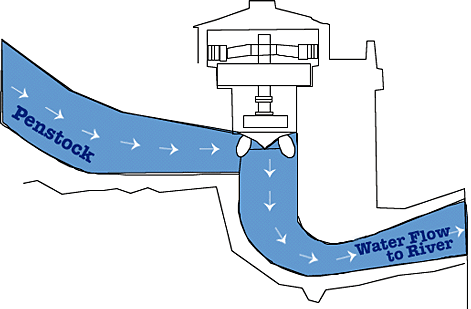
Click here for a graphic showing steps for generating hydropower.
Introduction
HYDROPOWER is a clean, low cost and renewable energy source that takes an unpredictable resource — rainfall and snowpack — and turn it into a reliable source of electricity. Hydroelectric projects can support recreation, irrigation, flood control, transportation and habitat needs.